Basics
Login & Analysis TypesPATENTS
Understand the Radar
Create an Analysis
Create a Data Set to Analyze
View Analysis
Find on Radar
DOCUMENTS
Understand the Radar
Upload Data to Analyze
Create an Analysis
View Analysis
Find on Radar
SCOPE
Understand the radar
Select Data Source
Create an analysis
On the Radar
Find on Radar
User Guide.
DOCUMENT Radar.
Understand the Radar
Documents in the data set are text mined and grouped together in clusters based on semantic similarities, or individual plots are created if an unclustered analysis is selected. Then they are run through multi-dimensional scaling and precisely positioned on a 2D radar based on their differences. Each dot represents one cluster or plot, with the size of the cluster reflecting the number of documents it contains. The closer the clusters the more similar their contents are. The XY axes have to particular meaning: distance is the focus of the data landscape.
Contour lines are created based on document density in areas of the radar, indicating possible semantic similarities or other levels of connectivity.
The analysis is automatically based on the company or organization that has the most documents in the data set: the Target Company. The others on the target list are the ones with the closest centers of gravity (overall document similarity) and filing ranges to the target company.
Get Started!
Upload Data for an Analysis
Select Documents → Start
Create a Data Set to Analyze: upload your file containing up to 100,000 documents as a .xlsx, .csv, .tsv, or .txt with character encoding UTF-8 or ASCII for English, Shift_JIS for Japanese, or UTF-8 for Chinese
NOTE
The first row must contain the field names, and for ideal performance and functionality, include an id, name, and timestamp. If no id, name, and timestamp are included, you can still proceed with the upload and analysis process, but some functions may not perform as intended. See images belowMedical Research Journals
Download a sample
Download a .CSV template.
Document Settings: After selecting your file for upload, you can view and customize its data-points as needed.
The system will automatically detect the ID (used for identifying documents), Name (used for labeling), and Timestamp (used for trend graphs and other time indicators) in the original file. You can change the target of these data-points by clicking the dropdown. If you want to undo a custom selection, select 'Include' on the dropdown.
All data-points will be included by default, and you can exclude any by clicking the dropdown and selecting 'Exclude'.
Data-point names can be customized by clicking the pen icon.
Click 'Ignore the first line of the file' if the required field names begin on the second line.
NOTE
If there are blanks or duplicates in the ID field, you will get an error. If this happens, adjust the file locally and make sure there are no duplicates or blanks.NOTE
Click "Ignore the first line of the file" if the required field names begin on the second lineRequest Data Set to start the upload or Cancel to return to the previous page.
Check Uploaded Data: confirms the success of an upload, or will give an error message indicating the cause of an unsuccessful upload. Click Go to Data Set to open the uploaded file. Click the Data Sets tab to view and select for analysis.
Create an Analysis
Uploaded data sets will be listed on the Data Sets page. To select a data set for analysis, click the box next to the data set name to add it to the Data Set list under Analyze. Then set the summary fields and field importance parameters (this controls what data will be included and how it will be calculated). Under Analyze, confirm the Data settings:
Analysis Name: enter the name you'd like to give your analysis. If left blank, an analysis number will automatically be assigned.
Data Set: selected data sets will be listed here. Total Documents gives the cumulative number of documents in all selected data sets.
Summary Fields: select the data fields for the following:
Organization: This is usually companies, assignees, or owning entities. This field is used to analyze gravity trends, document distribution, SWOT, and more.
Person: This is usually inventors, authors, or affiliated persons. This field is used for aggregation and relevant document volume counting.
Custom: This is usually IPCs, CPCs, or other document codes. This field is used for aggregation and relevant document volume counting.
Field Importance: assign a numerical value to each field to determine the level of importance during the similarity calculation.
0: Fields with 0 will be omitted from the calculation. Company names, person names, document codes, and numerical data typically can't be semantically analyzed, so you should set them to 0.
1: This is the standard value and should be used for most semantically analyzable fields. If all are set to 1, an unbiased calculation will be performed.
2-20: Customized levels of importance can be applied in the similarity calculation. For example, if field B is twice as important as A, then set A—>1 and B—>2.
Sampling Threshold: confirm the amount of documents to include in the analysis.
NOTE
If the total number of documents in the selected data sets is higher than the maximum allowed on your account, a calculated sampling will be extracted for the analysisNOTE
If multiple data sets are selected, only common fields will be used for analysis. For example, if Data Set A contains Abstract, Claims, and Inventor, and Data Set B contains Thesis, Claims, and Professor, then only Claims will be available. If they do not have any common fields, Summary Fields and Field Importance will be deactivated and you will not be able to run the analysisUse Options to apply custom rules to the analysis calculation.
Name Normalization is the aggregation of company or author names, document codes, or other custom fields. To apply a new rule, create and upload a file under the More dropdown → Name Normalization. Sample File
Field Delimiter allows you to specify the type of character that separates text strings in the data. If applicable, select the type of delimiter, e.g. colon (:), semicolon (;), bar (|) etc. for the targeted columns of the dataset.
Cluster Strength increases or decreases the cluster volume by adjusting the similarity threshold.
Strong → fewer clusters with more documents per cluster.
Weak → more clusters with fewer documents per cluster.
Cluster Count allows you to specify the exact number of clusters created during the calculation process. To create an unclustered analysis, enter the Total Documents number of the data sets you want to analyze. See Data → Data Set → Total Documents.
Word Importance is the adjustment of the level of relevance of certain words during the similarity calculation and clustering process. Words can be emphasized, weakened, or excluded. To apply a new rule, create and upload a file under the More dropdown → Word Importance. Sample File
Word Grouping puts synonymous words together and runs them as one in the calculation process. To apply a new rule, create and upload a file under the More dropdown → Word Grouping. Sample File
Indexical Analyzer controls the parameters of the 2D visualization according to the number of documents in the data set and the scope of their contents. If a data set broadly covers a topic or field, e.g. renewable energy, set it to broad. If it is specific, e.g. solar power energy storage and transfer, set it to specific. For document volume, low is less than 10,000. Average is 10,000-50,000. High is 50,000+.
Advanced Options: adjust calculation settings for Contour Lines, Gravity Distance Transition, and Noteworthy Areas.
Click Run Analysis to start.
Your Analysis is in Progress: view the status of your analysis here. When complete, you will be notified by email. You can leave this page without affecting the progress. You can check the status under My Analyses.
NOTE
Depending on the document volume, it can take a few minutes to several hours to run the analysisAfter running an analysis, it will be listed on the Create/Analyses page under My Analyses, and on All Analyses from the More dropdown.. You can hide, download, share, and delete analyses on this list.
View Analysis
Under My Analyses or from All Analyses, select the analysis you'd like to view.
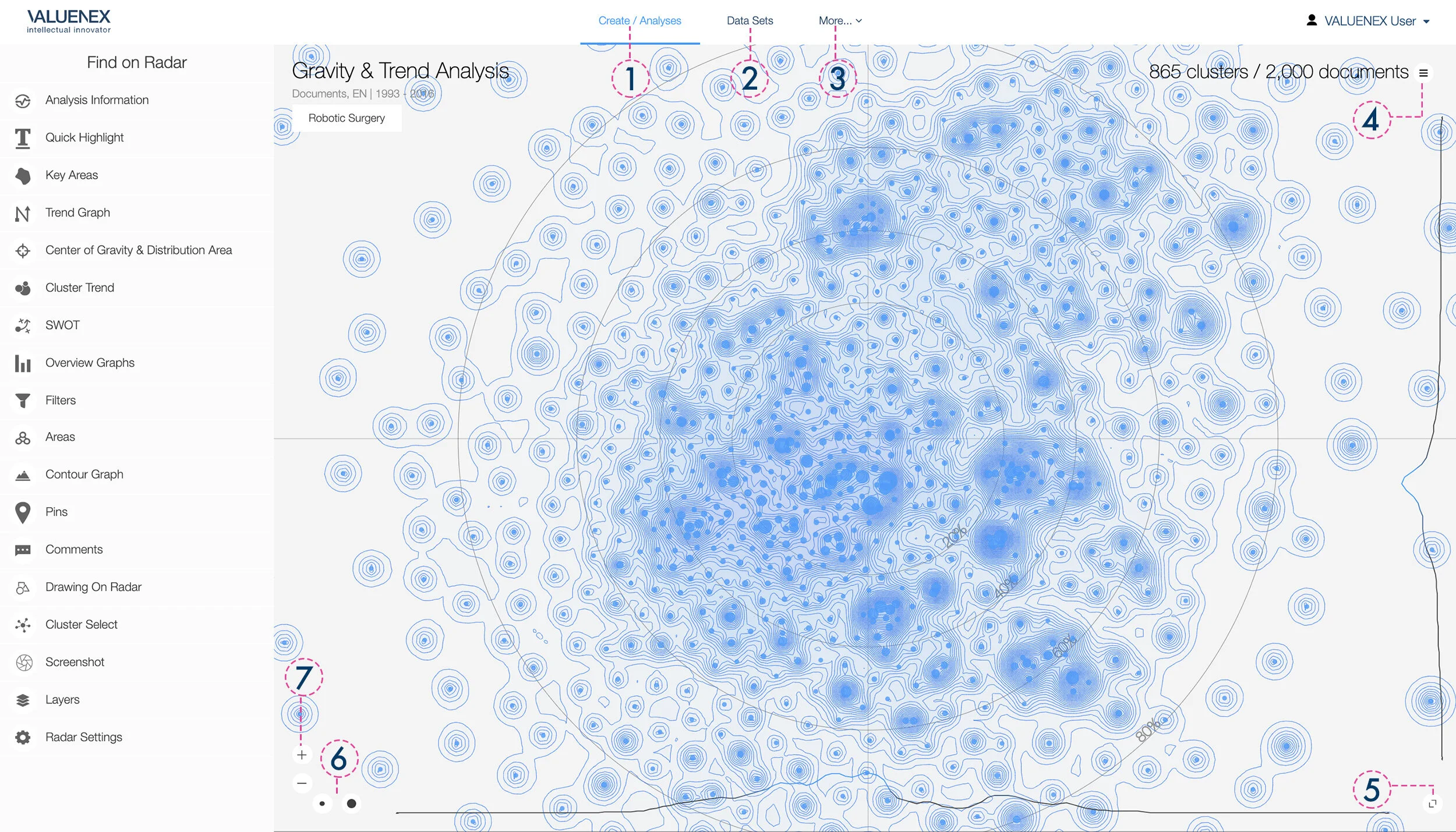
1. Return to your list of analyses or create a new one
2. Manage your data sets
3. Manage your word importance, word grouping, and name normalization files, and view your browsing history and license usage, or access your All Analyses page
4. Adaptive list: click to view all visible documents on the radar
5. Full screen
6. Cluster size control
7. Zoom
Adaptive List: contains all clusters and documents in the analysis and is located below the radar. The list adjusts based on Quick Highlight and Filter selections to show only the clusters you have highlighted on the radar.
1. Create a new data set, create a sub-radar, or view all documents on the list
2. Order by cluster size (number of documents in the cluster)
3. Order by distance from the center of the radar
4. Pin the cluster on radar
5. Expand to show the document details and position on an isolated radar
6. Number of documents in the cluster
Find on Radar
Analysis Information: view the metadata of the analysis, access contained data sets, and view statistical info of the analysis.
TARGET COMPANY is the basis for the SWOT analysis, Trend Graphs, Center of Gravity & Distribution Area, and Overview Graphs. Target company default is based on highest document volume, default Competitors List is based on closest proximity of center of gravity to the Target. Click the pop out icon to change, add, or delete Target or Competitors.
SHARE, PRINT, +SUBSET are also accessed here.
Quick Highlight: highlight or isolate clusters based on keywords, years, organizations, inventors/authors, or custom parameters.
OR displays the clusters that contain the selected item/s. (Cluster-based search)
AND displays the clusters that contain ALL of the items selected. (Cluster-based search)
IN isolates clusters containing individual documents with all selected data-points. (Document-based search)
FILTER displays ONLY the selected items.
UPDATE CONTOUR adjust the contours based on what is visible on the radar when Filter is activated.
SCALE adjusts the cluster size based on relevant document ratio and pre-selects the data-points on the cluster page based on your selected items. Single click on the circle next to the selected items to change the highlight color.
SELECTED brings selected items to the top of the list.
CLEAR erases all selections on Quick Highlight and returns clusters to default.
Key Areas: highlight major (high density), growing, or sparse (low density surrounded by high density) areas on the radar.
NOTE
Key Areas labels are off by default. To activate them, go to Layers → Key Areas and select.For additional indicators, activate the Noteworthy Areas layer.
M: Major: in or near highest contour peaks, G: Growing: indicating faster growth than other regions, S: Sparse: indicating lower density within higher density regions, N: Newer: based on Cluster Trend, U: Unique: based on Density Graph, W: Weakness: based on SWOT, P: Strength: based on SWOT
Trend Graph: shows the target and its competitors’ center of gravity movement over time range of the data set. Click on a company to view its trend graph, and single click on the circle next to the company name to change the highlight color.
NOTE
You can add or remove companies on the list by clicking Analysis Information → Target CompanyCenter of Gravity and Distribution Area: shows the overlap and distances between the target's patent distribution range and center of gravity compared to others in the data set. Single click on the circle next to the selected companies to change the highlight color.
Cluster Trend: highlight the clusters containing the newest documents, largest number of documents, and closest to the centroid of the analysis. Click to highlight on the radar. Single click on the circle next to the cluster number to change the highlight color.
SWOT: view the target company’s strong and weak areas (based on relative document volume, growth rate, uniqueness, and filing trend compared to others in the data set), its nearest assignee (the one with the most overall similar documents) and its caution assignee (the one moving fastest towards its center of gravity). Click to highlight on the radar. Single click on the circle next to the cluster number to change the highlight color.
Overview Graphs:
Density: shows the integration density of each cluster of the target company. X and Y axes are the integration density of target compared to others in the data set. The blue line is a least-squares method regression line. The red dotted lines are 3-sigma lines. The plots above the blue line are the target's strengths, those below are its weaknesses. The further from the axes origin the more unique. See SWOT above for more details.
Gravity Distance Transition: shows the transition of the distance between the target's center of gravity and the others', showing divergence or convergence trends over the time range of the data set. Target is represented by the X-axis.
Distance vs Trend: indicates the level of competitive caution of the target vs others. X and Y axes are the distance and trends between the target's center of gravity and the others' gravity. Positive and negative numbers indicate if their gravity is moving away from (+) or approaching (-) the target. Also see synergy classifications above.
Distance vs Radius of Area: shows the overlap and distances between the target's document distribution range and center of gravity compared to others in the data set. X-axis shows the area of distribution. Y-axis shows the distance between the target's gravity and the others. Plots to the left of the green line indicate an overlap with the target, while to the right of the line indicates none. Also see synergy classifications above.
Number of Applicants in documents: indicates the number of documents an applicant has in the data set.
Number of Inventors in documents: indicates the number of documents that an inventor is connected to in the data set.
Number of documents in IPCs: indicates the number of documents containing a specific IPC.
Number of documents in Applicant: indicates the number of documents an applicant has over the time-period of the data set.
Number of documents in Inventor: indicates the number of documents that an inventor is connected to over the time-period of the data set.
Number of documents in IPCs: indicates the number of documents containing a specific IPC over the time-period of the data set.
Filters: create and manage customized filters.
Name: enter filter name (required).
Color: select color.
Border Width: set 0 for a cluster fill. Set 1-10 to circle the cluster. The higher the number the thicker the circle.
Shared Filter: set ON to make filter shareable across all analyses.
Document-based: Will highlight clusters containing individual documents that match all conditions.
Cluster-based: Will highlight clusters whose combined data satisfy all conditions.
To create a filter: select the filter target → select the target operator → enter the condition value.
To apply multiple conditions: Click the plus mark (+) to add a new condition, and click the minus (-) mark to remove a condition. There is no limit on the number of conditions.
When applying multiple conditions, they are calculated in the order they are entered. The calculation flow and an example of output is as follows:
Condition 1 and Condition 2 = Output A
Output A and Condition 3 = Output B
Output B or Condition 4 = Output C
Output C and Condition 5 = Output
Output D is what will be the final value of the filter.
In other words: (((1 and 2) and 3) or 4) and 5 = OutputSave: click save to create and apply the filter.
CONDITION OPTION - NOTES:
Data sets: Enter the number located on the data set details pop-up on Data Sets page.
Cluster ID: Enter a numerical value
To view, edit, and delete shared filters, use Manage Shared Filters.
Areas: select and analyze areas on the radar.
Use Areas to select and view all documents in an area, create a new data set from documents in an area, or create a sub-radar based on the documents in an area.
Once an area is created, hover over the area and click Manage area to edit area information, create data set from area, create a sub-radar from documents in area, change the shape, angle, position of area, or delete area.
Contour Graph: shows the density of documents in areas of the radar.
Levels: sets the number of contour line intervals. The higher the number the sharper the contour regions.
Range: controls the displayed portion of Levels.
Factor: increases or decreases contour line detail in low density areas.
Create Areas from Lowest Contour Lines: shows keywords of lowest contour levels, and activates Areas function.
Update the Contours Automatically: adjusts the contour regions automatically based on Highlight selections.
Heat Map: controls contrast of the radar based on contour regions.
Reset: returns the settings to the default.
NOTE
If the Contour Region has a square outline, it can be removed by lowering the Factor Level, or increasing the Contour Range Threshold in Advanced Settings - accessible through Radar SettingsPins: contains a list of pins you have placed on the radar.
Comments: contains a list of comments you have placed on the radar.
Drawing on Radar: draw and label areas on the radar.
Snapshot Mode: hide icons, metadata, and Target Company on the radar. Use your OS screenshot function to capture the radar.
Layers: control the visible layers on the radar.
DYNAMIC ACTIVATION enables layers to automatically come on when relevant functions are opened, even if they have been deselected on the Layers list. For example, the Clusters layer will automatically come on when the Quick Highlights function is opened.
Cluster Select: lists the cluster(s) you have clicked on the radar, including key words, years, and documents, and lists the history and access count of clusters you have clicked on the radar.
Radar Settings: control the settings of the radar.
RADAR SCALE adjusts the degree of zoom.
CLUSTER SIZE adjusts the size of the clusters.
BACKGROUND COLOR adjusts the background of the radar.
MAIN CLUSTER COLOR adjusts the default cluster color.
SHOW CLUSTER BORDER adds a thin border around all clusters.
CLUSTER POP-UP gives the option for hover-over or right-click pop-ups of cluster content on the radar.
ADVANCED OPTIONS allows adjustment of the advanced calculation and visualizations settings.
CLEAR ALL will remove selections on Quick Highlight, Trend Graph, Center of Gravity & Distribution Area, Cluster Trend, SWOT, Drawing on Radar, and custom zoom and cluster size will return to default. Areas, Filters, Pins, Comments, and Text Plots will not be removed.
Competitor List
Determines the companies that are considered possible competitors against the Target Company, and are listed on Trend Graph, Center of Gravity & Distribution Area, SWOT, and Overview Graph functions.
Select Based on Volume to have the list be based on companies with the highest document volumes.
Select Based on Proximity to have the list be based on companies with the nearest centers of gravity (the focal point of a company's core document area) to Target Company.
*The default Target Company is the company with the most documents in the dataset. The default Competitors List contains the top 20 possible competitors based on document volume. You can adjust the Target or Competitors on the Analysis Information tab.
Contour
Contour Splits: Adjust the XY splits to increase or decrease the steps of the contour regions. The higher the number the sharper the regions.
Contour Range Threshold: Determines the % of documents in the data set that will be incorporated into contour regions, based on distance from the center of the radar.
Coefficient of Attenuation Function: Determines the interval of the counter lines. The higher the number the closer the lines are drawn.
* Contour lines can also be controlled directly on the radar. See Find on Radar → Contour Graphs.
Noteworthy Selection (Majority)
Sets the amount of cluster labeled with M (majority) on the radar. Majority represents clusters in or near the highest points of contour regions. Default of 10 means a maximum of 10 clusters can be labeled as ‘Major’.
* To view the output, go to Find on Radar → Layers → Noteworthy Areas and make sure it is on
Noteworthy Selection (Uniqueness)
Sets the amount of clusters by ratio labeled with U (uniqueness) on the radar. Uniqueness represents clusters in outlying areas. Default of 10 means a maximum of 10 clusters can be labeled as ‘Unique’.
* To view the output, go to Find on Radar → Layers → Noteworthy Areas and make sure it is on
Noteworthy Selection (Sparse)
Sparse represents regions of relatively low density compared to the surrounding high density areas. Adjust the XY Sparse Splits to increase or decrease the size of the mesh in the background of the radar that will be used to calculate ‘Sparse’ regions. The lower the numbers the larger the sections of the mesh, meaning there is a higher chance something might be labeled as ‘Sparse’.
Set the Sparse Range Threshold to the % of documents in the data set from the centroid to be incorporated into the calculation for 'Sparse'. The default 90% means the 91-100 percentile of documents furthest from the center of the radar will not be included in the calculation.
Noteworthy Selection (Newer)
Newer Target Date default is 1 year back from the date the analysis was created. Push the date back to increase the time range for ‘Newer’ regions, or bring it forward to decrease the time range.
Number of Selection in Newer sets the the amount of cluster by ratio labeled with N (newer) on the radar. Newer represents clusters containing the relative newest documents from the Newer Target Date. Default of 10 means a maximum of 10 clusters can be labeled as ‘Newer’.
* To view the output, go to Find on Radar → Cluster Trend → Newest
Noteworthy Selection (Growing)
Adjust the XY Growing Splits to increase or decrease the size of the mesh in the background of the radar that will be used to calculate ‘Growing’ regions. The lower the numbers the larger the sections of the mesh, meaning there is a higher chance something might be labeled as ‘Growing’.
Set the Growing Range Threshold to the % of documents in the data set from the centroid to be incorporated into the calculation for 'Growing'. The default 90% means the 91-100 percentile of documents furthest from the center of the radar will not be included in the calculation.
Set the Growing Threshold Date to the starting point of the period of interest. Default is 5 years back from the date the analysis was created. Push the date back to increase the time range for ‘Growing’ regions, or bring it forward to decrease the time range. If you are working with a short time range, you should adjust appropriately.
Number of Selection in Growing sets the the amount of cluster by ratio labeled with G (growing) on the radar. Growing represents clusters with the fastest relative increase in documents from the Growing Threshold Date. Default of 10 means a maximum of 10 regions can be labeled as ‘Growing’.
Gravity Distance Transition
Select to calculate and display the overall gravity trend on the Gravity Distance Transition Graph.
* To view the output, go to Find on Radar → Overview Graphs → Gravity Distance Transition Graph
If you cannot find your answers here, send us a message. Potentially found a bug? Let us know!