A Panoramic Landscape Across Space Tech
Published March 27, 2023 • 5 min read
From reusable spacecraft to innovative propulsion systems, space technology has made remarkable progress over the past two decades. By taking a look at the patent landscape of the space realm, we can begin to map out the most recent advancements relevant to space technologies and space exploration.
This panoramic analysis was created with a sample of the top 10,000 documents of 7,159,603 space-related patents based on a text query 1 , which were grouped into 2,482 clusters based on semantic similarities. These clusters were then mapped out based on their degree of similarity. With this output, from a time range of 2001-2022, we are quickly able to determine the major, growing, sparse (white space), and supplemental areas of R&D in the field. For clarity, the cluster layer in the images below was removed in order to put emphasis on the area densities represented in the heat map.
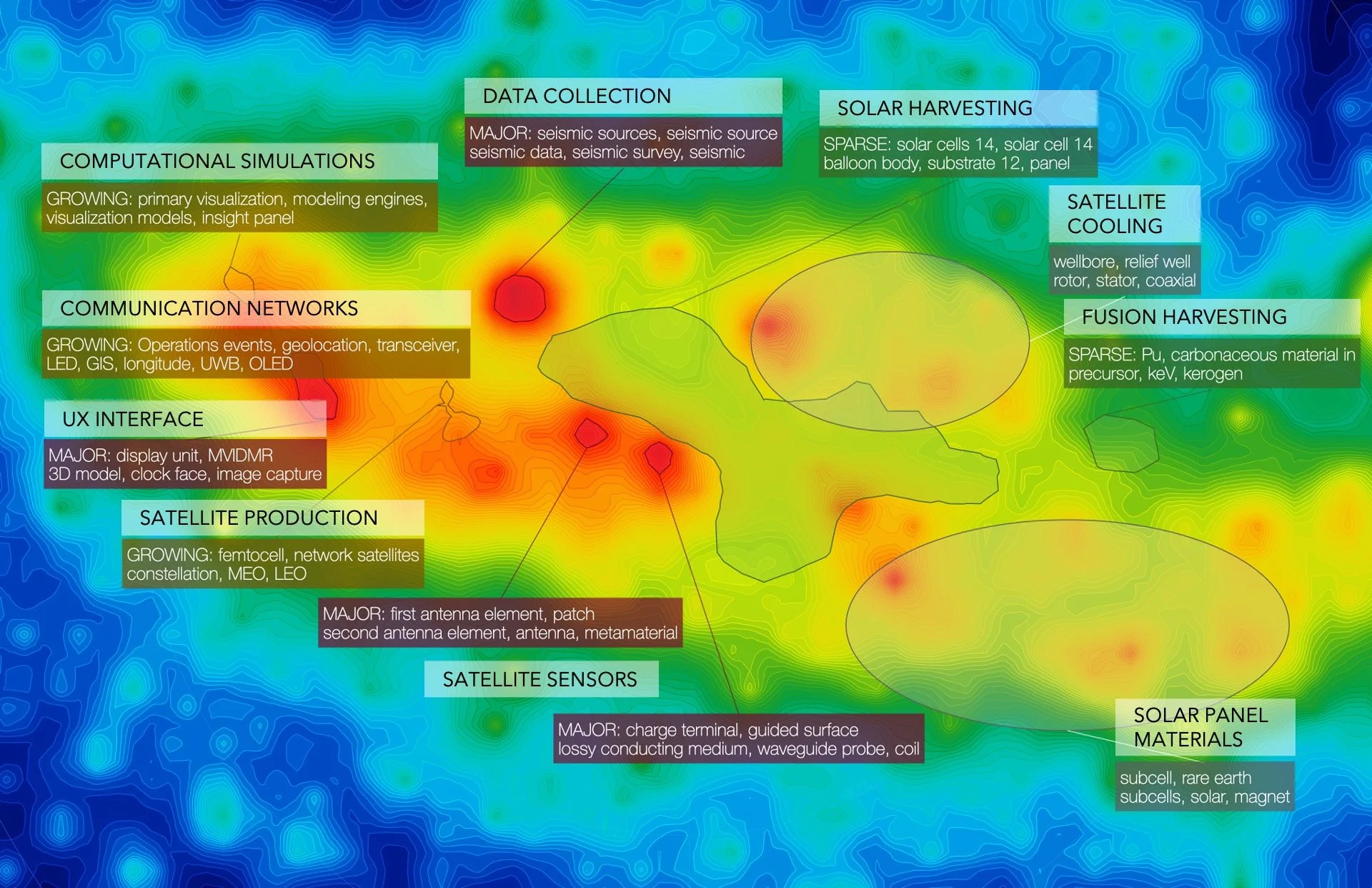
Fig 1 • Major, Growing, and Sparse Areas
In Figure 1, technologies related to UX Interfaces, Data Collection, and Satellite Sensors dominate the Major Areas which are all highlighted in red. Growing Areas (where filing volumes in recent years are higher than other areas) are those related to Satellite Production, Computational Simulations, and Communication Networks - key technologies necessary to improve the quality, safety, and overall effectiveness of systems to be launched into space. Lastly, Sparse Areas, which indicate potential opportunities for growth, are dominated by solar technologies and reactor-based energy solutions.
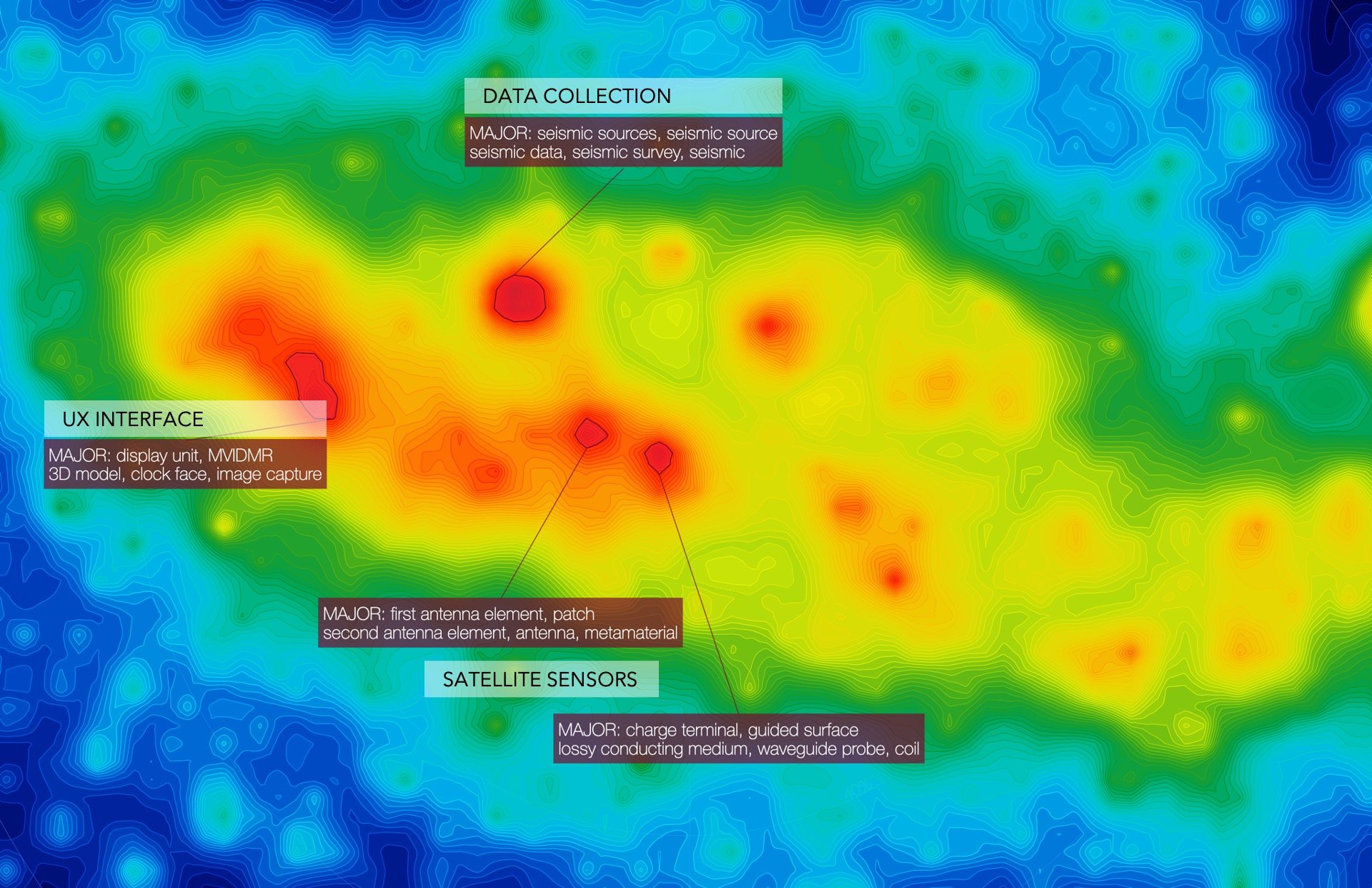
Fig 2 • Major Areas : primarily user-facing and data collection
The companies that filed the most patents in Major Areas were PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORP., DIGITALGLOBE, INC., SPACE SYSTEMS/LORAL, LLC, and RADIANT GEOSPATIAL SOLUTIONS LLC - each with at least 10 patents filed accordingly. Given that the analysis is centered around space technologies, the first four companies mentioned have recently filed patents related to processing relatively blurry images likely from satellites, which we can deduce after filtering the various clusters with keywords related to “user” as showcased in Figure 3. Furthermore, patents such as “SYSTEM AND PROCESS FOR COLOR-BALANCING A SERIES OF OBLIQUE IMAGES” and “VIEWPOINT PATH STABILIZATION” shows the need for stabilizing and processing the plethora of images taken from satellites.
In one area of particular interest among the major areas related to Data Collection, BP Corporation North America Inc. and Saudi Arabian Oil Company have the most patents assigned to them. In this major area, oil companies dominate which is likely due to leveraging space technologies to observe difficult areas where oil or other non-renewable fossil fuel resources otherwise would not be discovered or extracted. This may also be another method for how oil companies can further understand the detrimental effects their methodologies have on the surrounding environment (e.g., oil fracking).
Overall, technologies related to the UX Interface, Data Collection Methods, and the designing and manufacturing of satellite components dominate this space technology market, with various players filling in the Major Areas.
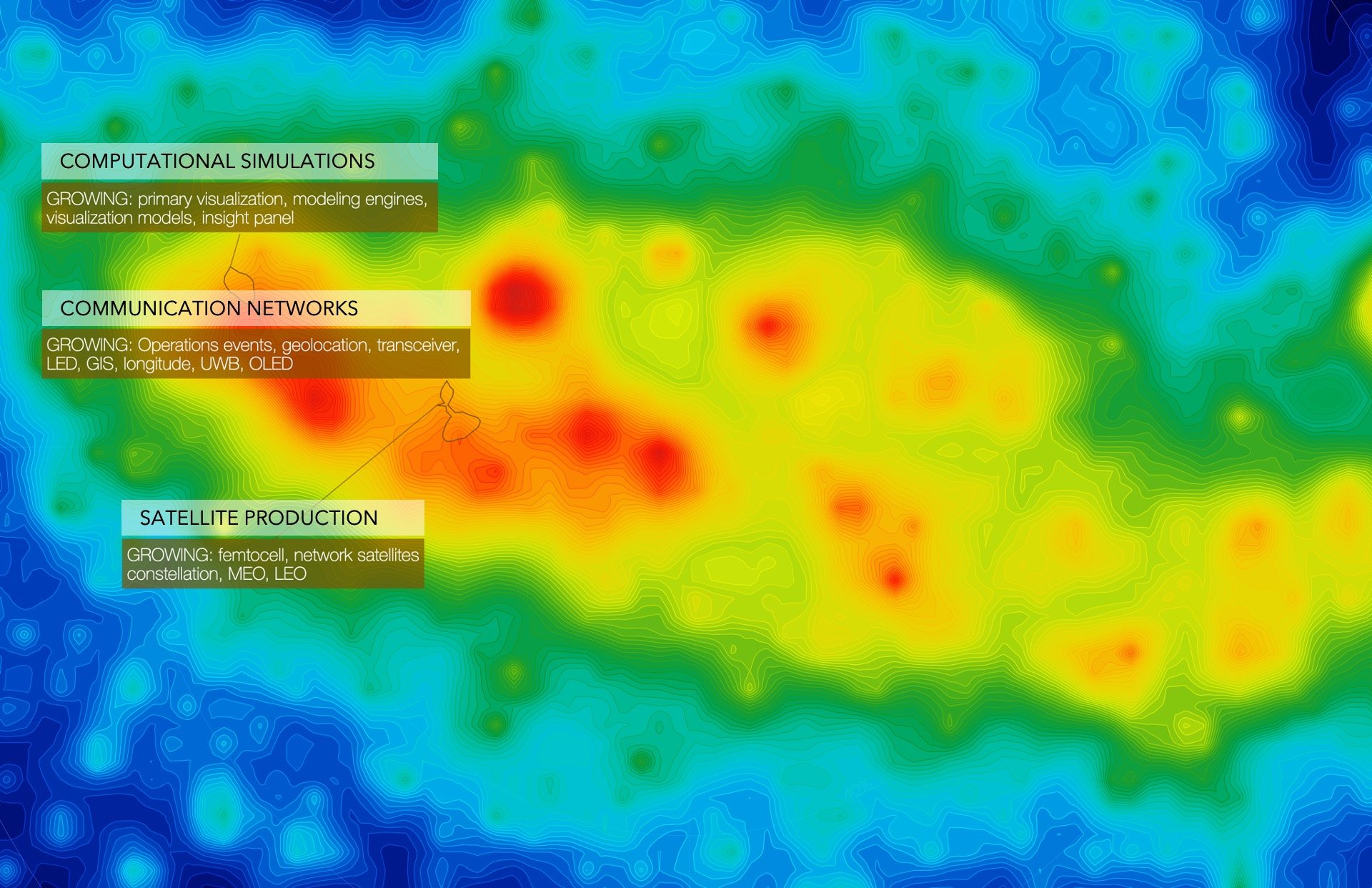
Fig 3 • Growing areas illustrate Computational Simulations, Communication Networks, and Satellite Production.
In the Growing Areas – which illustrates on Figure 3 activities that are likely to continue growing in the near future – technologies related to Computational Simulations, Communication Networks, and hardware related to Satellite Production reign supreme. The most prolific companies in this space are TABLEAU SOFTWARE, LLC and GLAS TRUST CORPORATION LIMITED with filing 4 and 3 patents respectively. For TABLEAU SOFTWARE, LLC, the company has recently filed patents focused on furthering the automation of data management systems and creating more interactive data analysis tools 2 . Furthermore, GLAS TRUST CORPORATION LIMITED filed patents related to reducing interference between satellites and ground based stations. 3
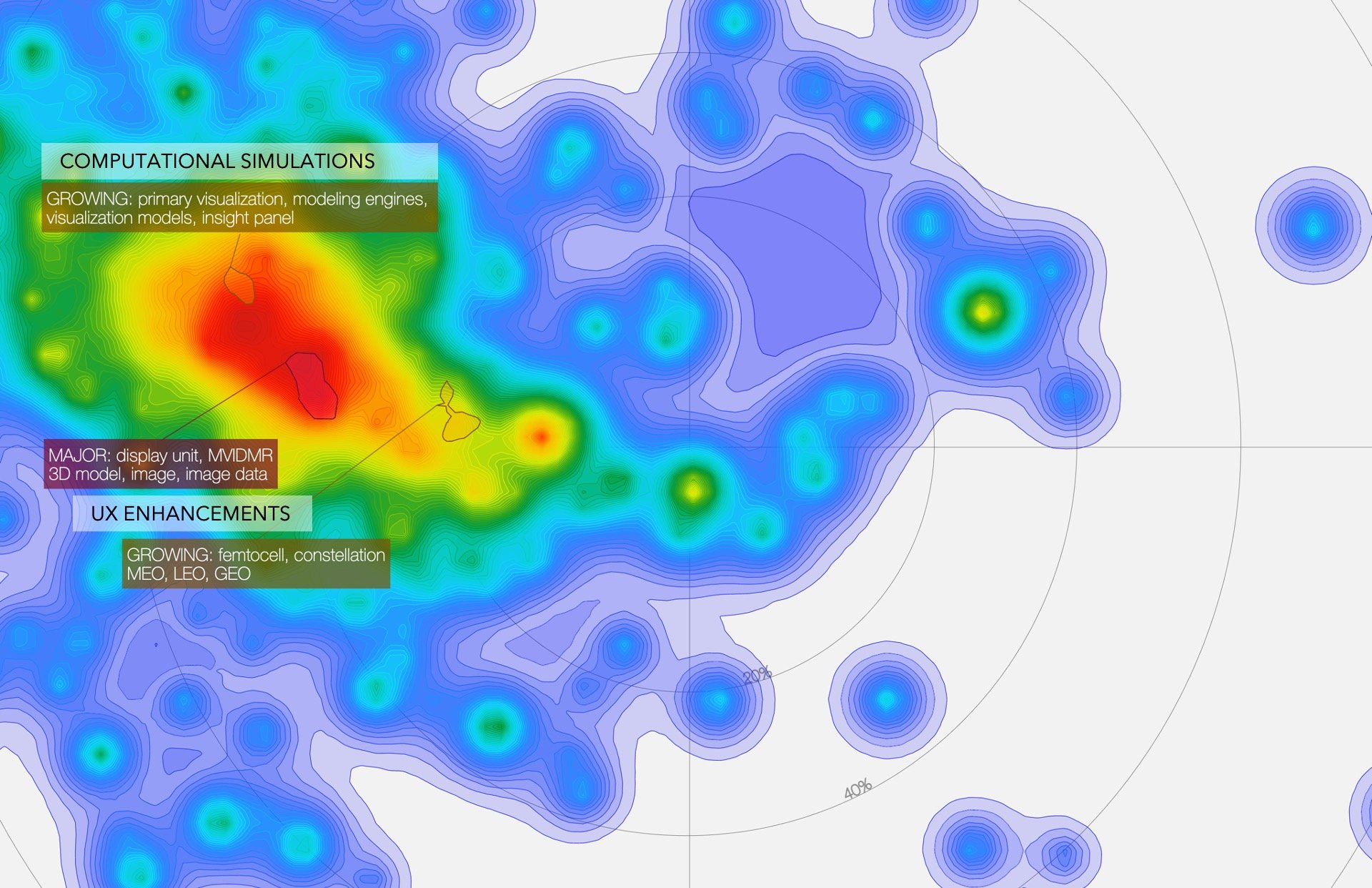
Fig 4 • Major and Growing Areas filtered with the keyword “user”
Further analysis within the growing areas showcased in Figure 4 illustrate increasing activities related to the digital space primarily in the form of computational simulations and UX enhancements. As mentioned, organizations like Tableau Software, a data analytics visualization software company, showcases this through some of its patent filings such as “CONTENT BASED RELATED VIEW RECOMMENDATIONS” explaining how leveraging machine learning intelligence is being developed within its line of product offerings in order to provide a more effective and efficient user experience when creating visually appealing graphs from largely text-based content. This is useful for space analysts to be able to more easily automate, optimize, and visualize graphs without having to be so concerned about manually editing every minute detail especially when analyzing large datasets.
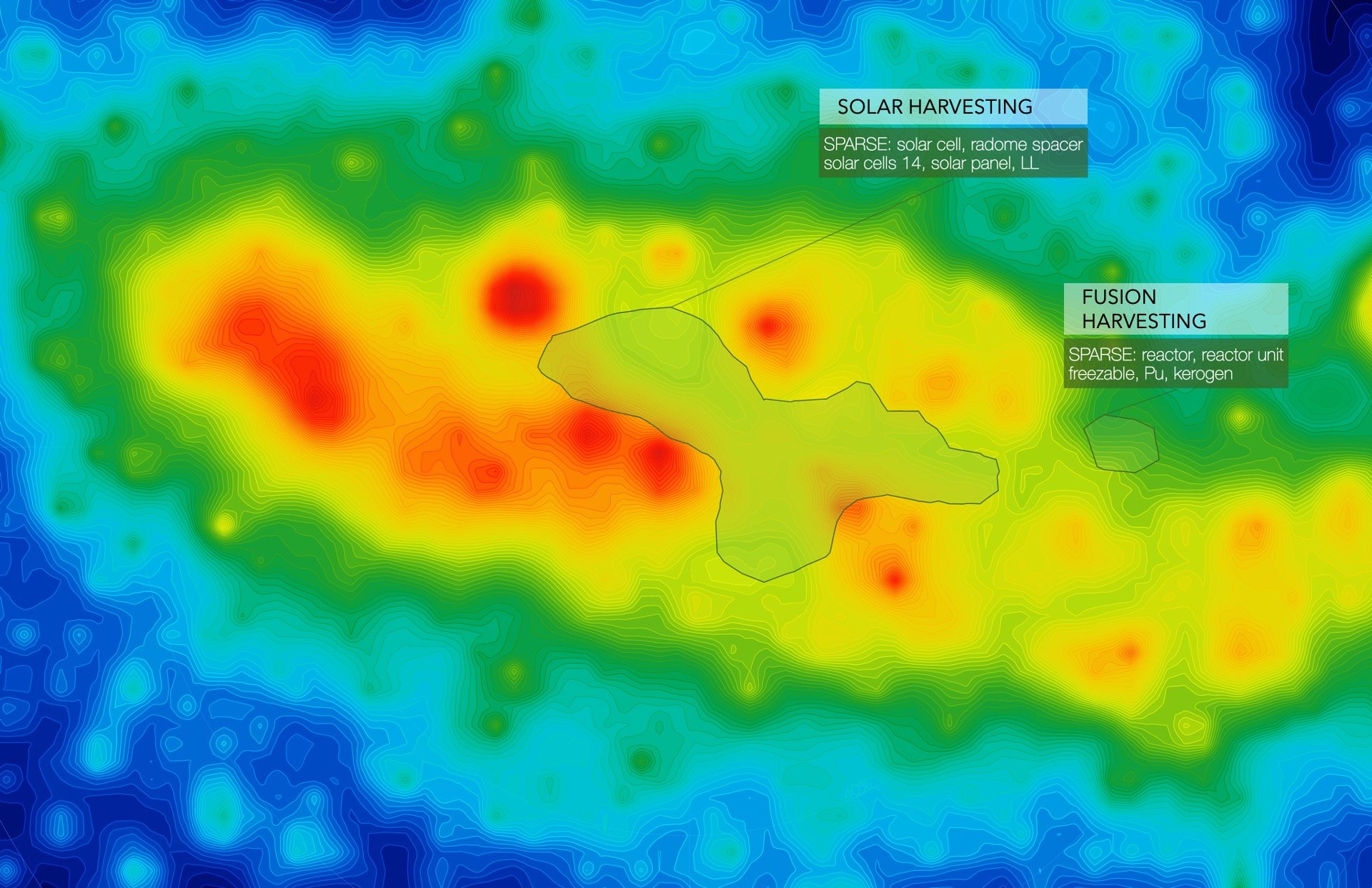
Fig 5 • Sparse Areas with a focus on Energy Harvesting
Looking through the sparse areas, the main topics or opportunities dominating this ‘white space’ or gaps within the markets are those related to Energy Harvesting via Solar and Fusion - technologies that primarily capture and harness energy. In these areas, organizations can take advantage of these opportunities to bridge the gap between major areas to the less saturated ones by manufacturing technologies or offering expertise that enhances existing power harvesting collection methods (namely solar and fusion-powered technologies) which may revolutionize the integrity, durability, and long-term reliability of space-related materials. Among these areas, companies such as MICROCHIP TECHNOLOGY INCORPORATED and KJT ENTERPRISES, INC, have 10 patents filed – the most in this field. Further analysis within the sparse areas illustrates the need to enhance energy production and consumption more effectively and efficiently 4 . Another recently-patented and noteworthy area is related to reactors, as there seems to be a need to convert animal (or human) waste into hydrothermal energy 5 , where the German company Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is working to develop into a reality. Overall, energy harvesting through various means presents unique opportunities for organizations to take advantage of the gaps in the market. There are few competitors in this space and it is possible that these regions will become much denser in due time.
Fig 6 • Supplemental areas carved out from the landscape
In addition to the auto-generated Major, Growing, and Sparse areas, supplementary areas were carved out to analyze additional regions of the analysis. The dominating topics in these areas are related to mining rare earth metals and climate change-related technologies. Among the circled areas shown in Figure 6, SOLAERO TECHNOLOGIES CORP (11 patents) and BAKER HUGHES HOLDINGS LLC (8 patents) specialize primarily as producers of electricity. Solaero produces solar cells for satellites and Baker Hughes produces oil-related products and services respectively. Under the “rare earth” bubble, patents such as “MULTIJUNCTION SOLAR CELLS WITH SHIFTED JUNCTION” and “RARE EARTH MAGNET AND PRODUCING METHOD THEREOF” further illustrates patents related to energy-related production. Under the “wellbore” circle, the company “SCHLUMBERGER TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION” dominates with 21 patents related to the production of oil, which are further illustrated by patents such as “Storing hazardous material in a subterranean formation.” Overall, the topics discussed in these spaces showcase topics similar to the sparse areas, where relatively few organizations are working to produce energy-related components and technologies needed to enhance the power consumption, production, and overall effectiveness as well as the long-term health of satellites and other future components, systems, and technologies.
Fig 7 • Market map for Space technology
Overall, the panoramic analysis has illustrated the various areas where patents reign supreme, the organizations actively working to turn their patents into reality, and the many ways space technologies are actively being developed.
Given the lack of knowledge society still has about space, there is a logical explanation behind why the major areas mainly focus on ‘space exploration’ such as satellites, data processing, and antennas. We predict, based on current trends for space technology, that the upcoming prominent field would be data management, and ensuring that the vast amount of space photos and accompanying data can be properly digitally stored and analyzed. The vast majority of companies focus on simply acquiring knowledge, but we believe that the future rests in utilizing the knowledge to its fullest. The industry of space technology is especially intriguing with how all areas interconnect with one another, with the sparse areas hinting at signs of companies preparing for more efficient methods of energy accumulation. The commercialization of space technology has led to companies requiring an optimal method of accumulating energy to send out satellites and rockets and acquiring patents behind this seems to be a key mission. As we continue to develop new technologies and capabilities, it is likely that we will see even more exciting patents emerge, and one day in the not-too-far future we might see the first spacecraft land on Mars incorporating some of the technologies seen in this patent landscape.